NIMHANS
National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences
Institute of National Importance, Bengaluru
National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), Bengaluru is a world-renowned centre of excellence in the realm of mental health and neurosciences. NIMHANS embodies a tripartite mission of delivering unparalleled patient care, conducting pioneering research, and imparting cutting-edge training.
The rich history of NIMHANS is intertwined with the evolution of mental health care, dating back to the 19 th century. One of the notable milestones was the founding of the Bangalore Lunatic Asylum in 1847. The asylum was renamed as Mysore State Mental Hospital in 1925, signifying a paradigm shift in the management of mental illnesses. This hospital and its counterpart in Ranchi, were the only two purpose-built asylums in British India in the early 20th century. They were designed with the explicit purpose of providing a healing environment, and with all the necessary modern attributes.
The turning point arrived in 1954 when the Government of India sanctioned the establishment of the All India Institute of Mental Health (AIIMH) based on the recommendations of the Mental Health Advisory Committee (in 1945) and the Bhore Committee (in 1946). This marked a significant step towards a more comprehensive and integrated approach to mental health care. The amalgamation of the Mental Hospital and AIIMH on 27th December 1974 resulted in the birth of NIMHANS, ushering in a new era and exemplifying the successful integration of various processes into a meaningful whole.
Spread across an area of 135 acres in the heart of the garden city, the central campus of NIMHANS combines mental health and neurosciences under one roof. Originally conceived as a tertiary care referral centre for mental, neurological and neurosurgical disorders, NIMHANS has surpassed its intended role. Its reputation for quality care has transcended borders, drawing patients not only from various parts of India but also from neighbouring nations. Serving more than half a million patients annually, NIMHANS employs therapeutic modalities that bridge modern medicine with traditional systems, fostering a holistic approach to healthcare. This fusion creates a unique therapeutic environment that caters to the diverse needs of its patients. The Institute houses nearly 20 specialized clinics, each tailored to provide disease-specific, patient-centric treatment.
The 1000-bed hospital, accredited by NABH, features state-of-the-art inpatient facilities and advanced rehabilitation services. Round-the-clock emergency and neurosurgical units are well-equipped to provide top-tier care for major head injuries. The seven-floor Sub-Speciality Block, with 125 beds and sophisticated operation theatres, stands ready to address complex neurological and neurosurgical problems.
Beyond its central campus, the Institute extends its reach and impact with facilities such as the Sakalwara Community Mental Health Centre and the NIMHANS Centre for Well Being in South Bengaluru. Demonstrating forward-thinking initiatives, NIMHANS is set to establish a poly trauma centre on the Kyalasanahalli campus in the northern part of the city –reaffirming its dedication to providing comprehensive care.
At NIMHANS, the pursuit of knowledge is relentless. Research occurs in a seamless manner from the bench to the bedside and from the bedside to the community, through active collaborations with prominent regional, national and international agencies. From addiction to Alzheimer’s; from imaging to intensive care; from brain injury to interventional neuroradiology; from disaster relief to deep brain stimulation; from stroke research to signalling in the brain; from rabies to retroviral infections; from youth mental health to yoga; from molecular genetics to mindfulness; from restoration to rehabilitation – the research contributions of NIMHANS are vast and varied.
As the leading post-graduate training centre in the country, particularly in mental health and neurosciences, NIMHANS offers over 90 courses including MCh, DM, MD, post-doc fellowships, doctoral studies, MPhil, MSc, diplomas and undergraduate courses in select disciplines. It is actively engaged with a diverse spectrum of health care practitioners and policy influencers to deliver various capacity building programs that add value and contribute
to improved outcomes for patients and the broader health system.
Playing a pivotal role in national policy and programming, NIMHANS has been at the forefront of shaping the mental health landscape in India. The District Mental Health Program, a flagship initiative of the Government of India, stemmed from the Bellary model of care piloted by NIMHANS. The Institute remains a driving force for strategizing, reinforcing, and innovating both institutional and community-based mental health care
services.
NIMHANS has made substantial contributions to the formulation of the National Mental Health Policy and has been a strong advocate for rights-based mental health care. As the designated nodal centre for the ambitious Tele MANAS (Tele Mental Health Assistance and Nationally Actionable Plan through States) program, the Institute continues to lead in innovative mental health service delivery.
Since its inception, NIMHANS has grown remarkably in stature and made conspicuous strides. The Union Government, recognizing its pre-eminent position, declared the Institute a ‘Deemed University’ in 1994. And, in 2012, NIMHANS was conferred the status of an ‘Institute of National Importance’ through a separate act of Parliament. NIMHANS is consistently ranked among the country’s best by respected ranking agencies. These accolades bear testament to the Institute’s unwavering commitment to excellence in patient care, training, and research.
The Evolution
1850
Bangalore Lunatic Asylum
1935
Mysore State Mental Hospital
1954
All India Institute of Mental Health (AIIMH)
1974
NIMHANS: Amalgamation of State Mental Hospital and AIIMH
1994
Deemed University
2012
Institute of National Importance
Milestones
1975
Community Mental Health Services at Sakalwara; and Neuropathology Museum
1977

Family Wards
1979
 Central Animal Research Facility (CARF)
Central Animal Research Facility (CARF)
1982
 Electron Microscopy Lab (Neuropathology Dept.)
Electron Microscopy Lab (Neuropathology Dept.)
1985
 Psychiatric and Neuro Rehabilitation Services
Psychiatric and Neuro Rehabilitation Services
1987
 Comprehensive OPD complex
Comprehensive OPD complex
1991
 De-Addiction Centre
De-Addiction Centre
1995
Human Brain Bank
1999
 Digital Subtraction Angiographic (DSA) facility
Digital Subtraction Angiographic (DSA) facility
2001
CGC New Ward
2002
New Advanced Centre for Ayurveda
2005
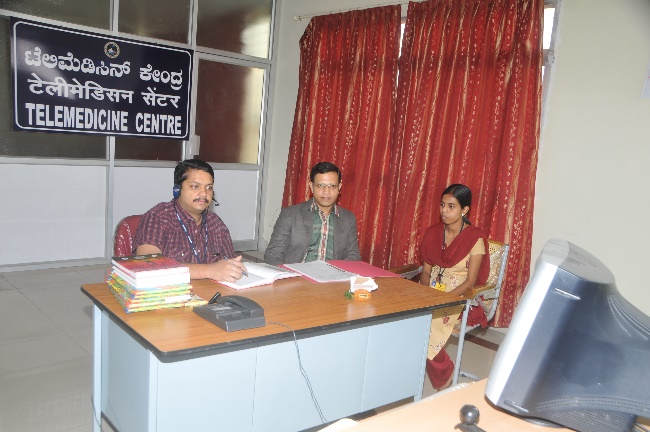 Telemedicine Centre
Telemedicine Centre
2006
Gamma Knife Facility
2007
 Advanced Center for Yoga
Advanced Center for Yoga
2010
 Neurobiology Research Centre (NRC);Cognitive Neuroscience Centre
Neurobiology Research Centre (NRC);Cognitive Neuroscience Centre
2011
Inventa Critical Care Ventilator; NIMHANS Centre for Well Being (NCWB);New Digital Subtraction Angiographic (DSA) facility
2012
 Centre for Public Health (CPH); MVG Block
Centre for Public Health (CPH); MVG Block
2013
Advanced Magneto Encephalography (MEG)
2014

ICMR Advanced Centre for Translational Research; NIMHANS Heritage Museum
2015
 State-of-the-art MR PET Scan Centre; Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Research Centre
State-of-the-art MR PET Scan Centre; Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Research Centre
2016
 Centre for Brain Mapping (CBM), Clinical and Research facility for EEG studies; Adolescent Psychiatry Centre (APC)
Centre for Brain Mapping (CBM), Clinical and Research facility for EEG studies; Adolescent Psychiatry Centre (APC)
2017
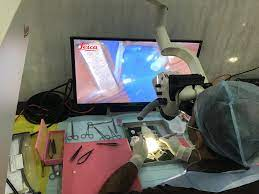
Microsurgical Skills Lab Surgical & Assistive Robotics
2018
Intraoperative MRI Operation Theatres; Medical Cyclotron Facility; Dr. RM Varma Sub-Speciality Block for Neurosciences NIMHANS Integrated Centre for Yoga (NICY)
2018
 First-Contact Psychiatry OPD Service; NIMHANS Digital Academy (NDA)
First-Contact Psychiatry OPD Service; NIMHANS Digital Academy (NDA)
2019
 NIMHANS Telemedicine Centre (Upgraded)
NIMHANS Telemedicine Centre (Upgraded)
2020
 Centre for Consciousness Studies; Autoimmune Laboratory; Construction of OPD complex at North Campus initiated
Centre for Consciousness Studies; Autoimmune Laboratory; Construction of OPD complex at North Campus initiated
2021
 NABH accreditation
NABH accreditation
2022
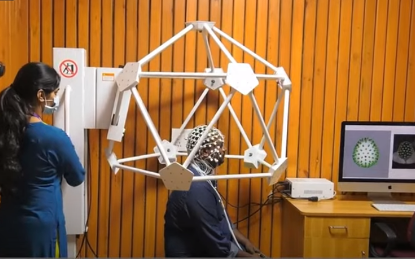 Gamma Knife Icon, cranial radiosurgery system
Gamma Knife Icon, cranial radiosurgery system
